Accounting or accountancy is basically the measurement, interpretation, and reporting of financial and/or non-financial information about financial entities including corporations and businesses. Financial accounting practices are conducted to provide information that can be used to make decisions about the allocation of resources of a company or enterprise. In other words, accounting provides information that is used to make the best possible management decisions for a business or organization. This includes the systematic recording, summarizing, predicting, measuring, and communicating of information regarding the financial performance of the organization and its various activities.
Accounting practices in accounting forms the basis of the fundamental principles that guide the conduct of business activities. Therefore, accounting has become one of the most important elements of business activity and has played a crucial role in the economic development of many countries. The need for accurate and reliable data in accounting has led to the development of numerous techniques and methods for the accounting of companies and enterprises. These techniques and methods are implemented in order to facilitate the effective collection, recording, interpretation, reporting, and management of the data that are essential for accounting. There are two broad areas in which companies must focus their accounting efforts, these include:
Management of Accounting: Accounting is concerned with the management of the financial statements of a company or enterprise. As such, it provides managers and other senior managers with the information necessary for them to make sound business decisions. The accounting profession helps managers to understand the financial statement and its implications as well as to implement the necessary changes to improve the performance of the business. To achieve this end, accounting professionals must be well versed in accounting principles, accounting policies, principles and practice.
Managerial Accounting: In managerial accounting, an accountant is primarily concerned with assessing and maintaining the financial performance of a business unit. Its aim is to meet the needs of management by providing timely and accurate financial reports. It helps businesses to take decisions about resource allocation. Some of the basic accounting principles that are related to managerial accounting are: the balance sheet, cash flow, short term financing, budgeting, gross profit, net profit and cost.
Cost Accounting: Cost accounting is a subset of managerial accounting that focuses on the identification, measurement, and reporting of costs and services delivered by the business. Cost accounting differs from accounting in that it addresses issues specific to the cost of doing business, such as the effect of waste and the absence of market entry. Some of the major activities covered under the scope of cost accounting are: analyzing cost savings opportunities, identifying and describing service needs, measuring and comparing prices charged by customers, monitoring and tracking productivity, planning and delivering services, and estimating costs associated with operating procedures. Cost accounting therefore requires knowledge of specific principles applicable to cost reduction activities, such as pricing, quality management, cost accounting software, and the principles of enterprise information systems.
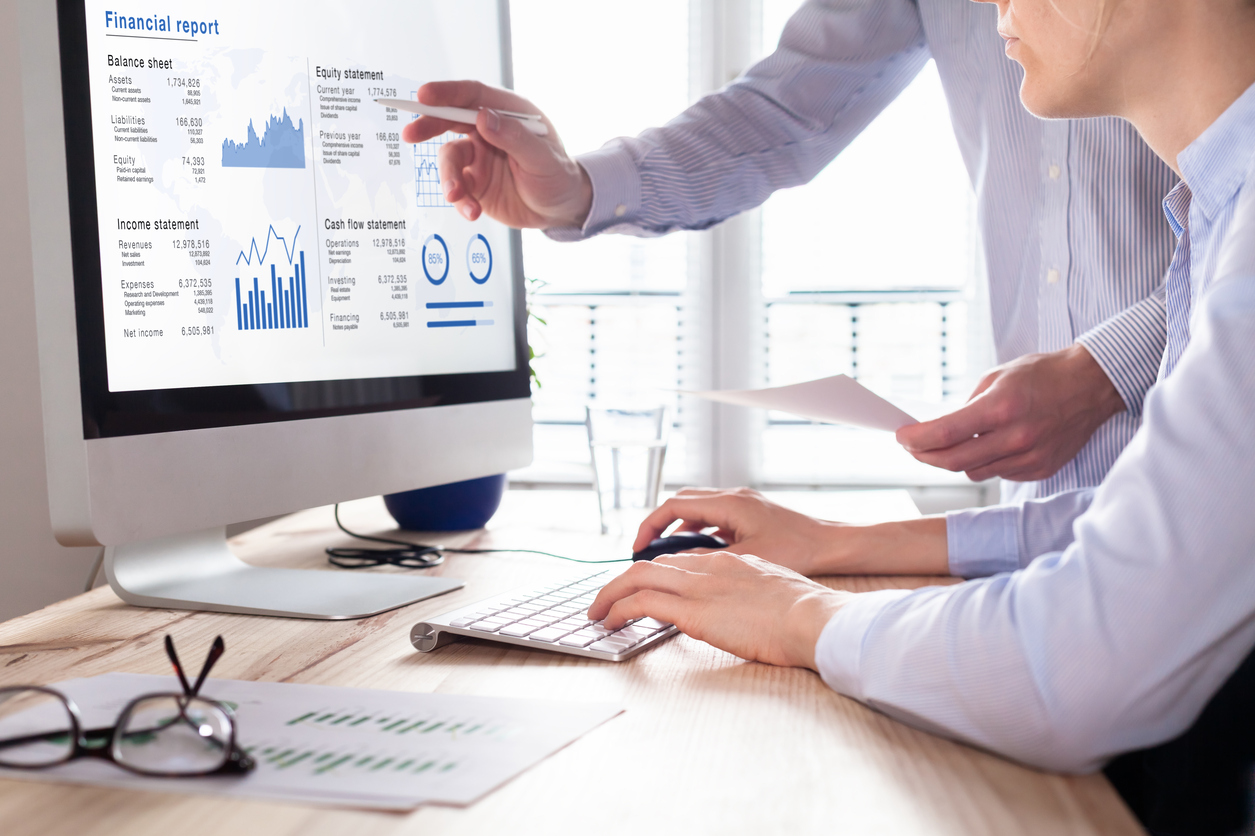
Financial Accounting: Financial accounting is prepared in accordance with guidelines prescribed by the GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles). This includes principles that are needed to determine the financial performance of an entity, its assets, liabilities, ownership interest and equity and other aspects of the business. The purpose of this aspect of accounting is to meet the requirements of shareholders, who must be given reliable and accurate information regarding the company’s financial performance so that they can make informed decision regarding its future. The primary objective of this aspect of accounting is to provide timely and accurate information to shareholders in order to facilitate decision-making.